
Being overweight can be risky for people’s overall health, but a particular type of fat, called visceral fat, can be especially dangerous.
Visceral fat is the fat that accumulates around your waistline, and it's more deeply set into your abdomen than subcutaneous fat that settles in other areas of your body.
In a recent issue of the Journal of Clinical Investigation discusses the dangers of visceral fat, including an increased risk of insulin resistance and heart disease.
✧ Eat healthily to get rid of visceral fat.
✧ Reducing your portion sizes, total calories and amount of saturated fat you eat can help you lose weight overall, according to the Mayo Clinic. Some of the bulk you lose will most likely come from your midsection.
✧ Focus on including whole grains, fruits, vegetables and lean protein in your diet.
People may tell themselves that the extra accumulating pounds around the waistline is an inevitable fact of aging, but research now tells us that as midsections grow, so does the dangerous health risks associated with cardiovascular disease and other organ problems.
Abdominal, or visceral, fat is of particular concern because it’s a key player in a variety of health problems — much more so than subcutaneous fat, the kind you can grasp with your hand.
☛ This has been linked to metabolic disturbances and increased risk for cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes.
☛ In women, it is also associated with breast cancer and the need for gallbladder surgery.
Where fat ends up is influenced by several factors, including heredity and hormones.
As the evidence against abdominal fat mounts, researchers and clinicians are trying to measure it, correlate it with health risks, and monitor changes that occur with age and overall weight gain or loss.
The good news is that visceral fat yields fairly easily to exercise and diet, with benefits ranging from lower blood pressure to more favorable cholesterol levels.
The pinchable stuff — can be frustratingly difficult to budge, but in normal-weight people, it’s generally not considered as much of a health threat as visceral fat is.
Research suggests that fat cells — particularly abdominal fat cells — are biologically active. It’s appropriate to think of fat as an endocrine organ or gland, producing hormones and other substances that can profoundly affect our health.
Although scientists are still deciphering the roles of individual hormones, it’s becoming clear that excess body fat, especially abdominal fat, disrupts the normal balance and functioning of these hormones.
Visceral fat is different from other body fat.
Subcutaneous fat, on the other hand, is body fat that is close to the skin's surface and is considered less dangerous, and easier to lose, than visceral fat.
✧ Studies have shown that those with visceral fat are more susceptible to heart disease, stroke, diabetes, and hypertension.
✧ Sedentary people, smokers and drinkers have been shown to have more intra-abdominal fat, or visceral fat, than active people who are non-smokers and non-drinkers.
✧ Stress may also be a factor in the storage of visceral fat on the body.
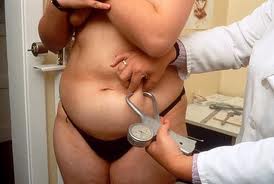
Visceral fat is harder to lose than subcutaneous fat because it is more deeply embedded in the body's tissues. It is only measured accurately by an imaging machine that can see how much of the abdomen is made up of visceral fat.
A person may be within a healthy weight range, but still have too much intra-abdominal fat around the internal organs.
The liver metabolizes visceral fat and releases it into the bloodstream as cholesterol. Harmful or "bad" cholesterol, which is Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL), builds up into a plaque that blocks the arteries.
Losing weight through proper diet and effective exercise can help reduce visceral fat. How much fat a person eats does matter as studies have shown that those who eat 30% or more of their diets as fat usually have high amounts of visceral fat.
Results from a 2005 Duke University study found that people who performed high-intensity aerobic exercise (jogging)--up to 20 miles weekly, lost visceral fat.
The Mayo Clinic adds that exercising in conjunction with actively losing weight can help melt the belly bulge. Scientists are also learning that visceral fat pumps out immune system chemicals called cytokines — for example, tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 — that can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
These and other biochemicals are thought to have deleterious effects on cells’ sensitivity to insulin, blood pressure, and blood clotting.
Substances released by visceral fat, including free fatty acids, enter the portal vein and travel to the liver, where they can influence the production of blood lipids.
Visceral fat is directly linked with higher total cholesterol and LDL (bad) cholesterol, lower HDL (good) cholesterol, and insulin resistance.
Insulin resistance means that your body’s muscle and liver cells don’t respond adequately to normal levels of insulin, the pancreatic hormone that carries glucose into the body’s cells. Glucose levels in the blood rise, heightening the risk for diabetes.
The starting point for bringing weight under control, in general, and combating abdominal fat, in particular, is regular moderate-intensity physical activity, over 60 minutes per day, to control and maintain weight.
But unfortunately, spot exercising or spot reduction, such as doing sit-ups, will tighten abdominal muscles over time, but will not zap the visceral fat.
Ask any bodybuilder or bikini fitness model and they will say something like "80 percent nutrition and 20 percent exercise" is the key to burning stubborn belly fat.
Everything you consume will become you and your body, so you need to be conscience of portion size, and emphasize complex carbohydrates (fruits, vegetables, and whole grains) and lean protein.
Refrain from eating processed and fast foods, mainly simple carbohydrates such as white bread, refined-grain pasta, and sugary drinks.
Replacing saturated fats and trans-fats with polyunsaturated fats will help shrink stubborn fat as well.
Spend time to prepare your meals and set yourself up for success. But don't forget the importance of nutrition in shrinking (whole body) belly fat.
Though the term might sound dated, “middle-age spread” is a greater concern than ever. As people go through their middle years, their proportion of fat to body weight tends to increase — more so in women than men.
Weight training is touted as the cure for many ills. But if the goal is to lose belly fat, aerobic exercise is the only way to go, exercise scientists say.
We're not talking about muffin tops, the annoying bit of bread that is baking in your midsection that rolls over a person’s waistline. Rather, this is gut fat lodged around internal organs, which could look like a beer belly from the outside. This is considered a risk factor for diabetes, heart disease, and cancer.
Reduce the amount of food that is consumed every day, and also improve the quality of food eaten.
Food that his high in sugar (usually processed) should be avoided – (pasta, breads, soda, cookies, cakes, candies, baked goods and other boxed sweets).
Eat mostly healthy green salads, colorful vegetables, fruits, lean and clean protein, and a variety of seeds and nuts. These types of food have a high nutrition to calorie ratio.

Studies have shown that intensive cardio exercise is more effective at burning fat than gentle exercise (i.e. jogging and walking).
Try interval training with jump ropes and plyometrics.
Lifting weights burn a lot of calories to help lose weight.
Compound exercises also work best as these work several muscle groups in unison, increasing the effectiveness of the workout and the weight loss potential.

It also builds muscle which requires more energy than fat to maintain itself and it increases metabolism.
Getting a good night’s sleep is often overlooked as a way to lose weight, but research has shown that people that do not sleep enough are more likely to gain weight, and it has little to do with the fact that tired people eat more. Aim for 7-8 hours each night.


This helps you to improve your workouts when you can see your goals and accomplishments as well as manually track them down and hold yourself accountable in recording the sessions and results.

This helps to highlight problem foods and problem times during the day. People do not realize all the foods and snacks they consume unless they are writing it down and can look back daily on what they have consumed.

This includes martial arts, yoga class, boot camp, or a personal or team fitness competition, as this will keep you more motivated and engaged with the “fun” aspect of physical wellness.
To get advice on empowering yourself to lose weight is also a great option.
They do not always work, can lead to nutritional deficiencies and are not sustainable.
Remember that nutritional and physical wellness is a lifestyle change, not a quick fix. This may not be as easy as taking a pill for 2 weeks or drinking pepper water or tea for 30 days.

It will be hard work and test our willpowers and challenge our determination. If health and wellness become part of your everyday life, you will begin to love exercising, educating yourself on how to be optimally well and be happier and more satisfied in many aspects of your life.
sources: dr.oz.com, peertrainer.com, WebMD.com, livestrong.com
